Deep Learning
1. What is deep learning?
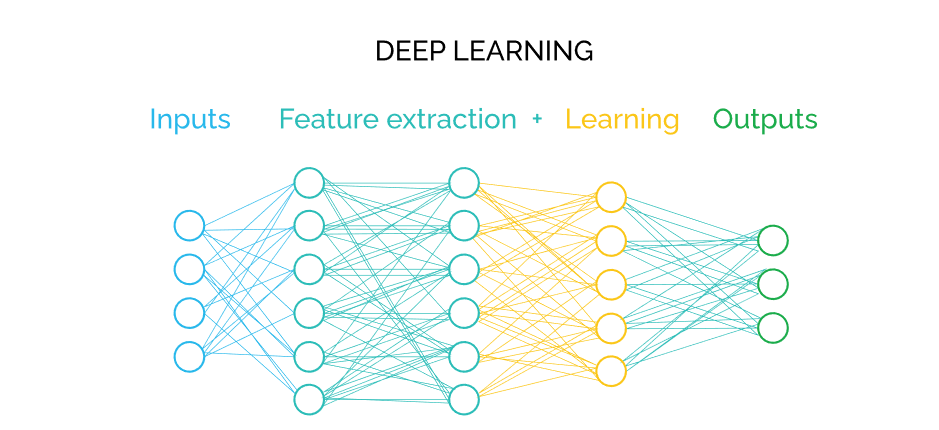
Deep Learning is a subset of machine learning that involves training artificial neural networks to perform tasks by learning patterns from data. These neural networks are composed of multiple layers (hence the term “deep”), and they learn to extract hierarchical features and representations from raw data, enabling them to make complex predictions or decisions.
2. Why is deep learning important?
Deep Learning has become crucial due to its ability to handle complex and unstructured data, leading to advancements in various fields. Its importance lies in its capacity to automatically learn relevant features from data, enabling tasks like image and speech recognition, natural language processing, and medical diagnoses with remarkable accuracy.
3. How does deep learning work?
Deep Learning involves the following key steps:
- Architecture: Design neural network architecture with multiple layers (input, hidden, output) that learn hierarchical features.
- Training: Train the model using labeled data, adjusting weights through backpropagation to minimize prediction errors.
- Activation Functions: Use activation functions to introduce non-linearity and enable complex learning.
- Loss Function: Define a loss function to quantify prediction errors and guide the learning process.
- Optimization: Use optimization algorithms (e.g., gradient descent) to update weights and minimize the loss function.
- Validation: Validate the model’s performance on unseen data to ensure generalization.
4. What are the most important use cases of deep learning?
Deep Learning is applied in numerous domains, including:
- Computer Vision: Object detection, image classification, facial recognition, and autonomous driving.
- Natural Language Processing: Sentiment analysis, machine translation, chatbots, and text generation.
- Speech Recognition: Voice assistants, transcription services, and speaker identification.
- Healthcare: Medical image analysis, disease diagnosis, drug discovery, and personalized treatment.
- Finance: Fraud detection, algorithmic trading, credit scoring, and risk assessment.
- Automated Gaming: Playing games like chess, Go, and video games at a high level of expertise.
- Autonomous Systems: Self-driving cars, drones, and robotics for navigation and decision-making.
- Recommendation Systems: Product recommendations, content recommendations, and personalized marketing.
- Industrial Automation: Predictive maintenance, quality control, and process optimization.